目次
- 1 試験概要と流れ
- 2 トレーニング手順
- 3 スピーキング対策:5つの質問
- 4 質問 1: How do natural disasters affect the global economy?
- 5 質問 2: Should governments provide subsidies to struggling industries?
- 6 質問 3: What is the impact of income inequality on society?
- 7 質問 4: How do online shopping platforms affect traditional brick-and-mortar stores?
- 8 質問 5: Is globalization beneficial or harmful to local economies?
- 9 まとめ
試験概要と流れ
- 入室
- 「面接カード」を渡す
- 着席
- 氏名の確認と簡単な日常会話
- 「トピックカード」を受け取る:様々な分野が混ざっている
- スピーチ準備(1分間)
- スピーチ(2分間):概ね180〜240語(話すスピードによって異なる)
- Q&A(4分間)
スピーチの内容に関する2-3の質問 - 「トピックカード」返却
- 退室
トレーニング手順
- カテゴリー(分野)毎に観点とキーワード整理(10分程度)
- 実際にスピーチをして録音して聞き直す(2分+聞き直し)
- 満足できるまで数回繰り返す
- カテゴリー別に話せる様になったら本番形式(トピックが混ざったカード)でトレーニングを行う
スピーキング対策:5つの質問
トレーニング用に同じ分野のトピックを5つ記載していますが、実際のトピックカードは、5つの異なる分野から出題されます。
- How do natural disasters affect the global economy?
- Should governments provide subsidies to struggling industries?
- What is the impact of income inequality on society?
- How do online shopping platforms affect traditional brick-and-mortar stores?
- Is globalization beneficial or harmful to local economies?
- 自然災害は世界経済にどのような影響を与えますか?
- 政府は困難な状況にある産業に補助金を提供すべきでしょうか?
- 所得格差が社会に与える影響は何ですか?
- オンラインショッピングプラットフォームは従来の店舗にどのような影響を与えていますか?
- グローバリゼーションは地域経済にとって有益ですか、それとも有害ですか?
質問 1: How do natural disasters affect the global economy?
(自然災害は世界経済にどのような影響を与えますか?)
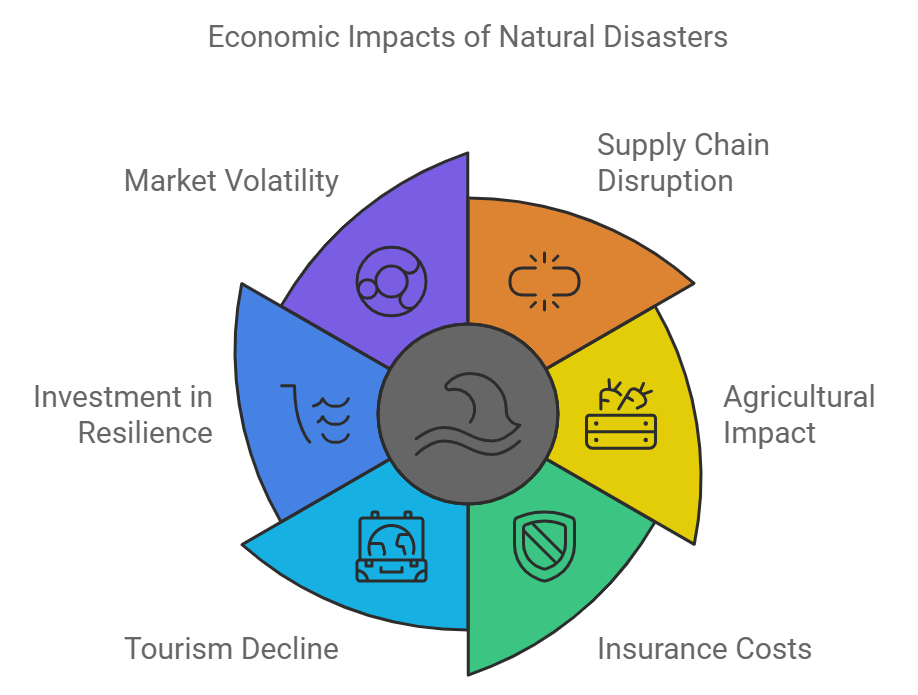
観点 (Perspectives)
- Disruption of Supply Chains (サプライチェーンの混乱)
- Natural disasters often disrupt global supply chains by damaging infrastructure such as roads, ports, and factories. This can delay the production and delivery of goods, leading to shortages, price increases, and economic slowdowns in industries reliant on affected regions.
- Impact on Agriculture and Food Security (農業と食料安全保障への影響)
- Many natural disasters, including floods, droughts, and hurricanes, devastate agricultural land, reducing crop yields and disrupting food supply chains. This can lead to global food price inflation, impacting both producers and consumers, particularly in low-income countries.
- Insurance and Recovery Costs (保険と復旧コスト)
- The financial burden of natural disasters is significant, with insurance companies often facing huge payouts. Governments must also allocate substantial resources for recovery efforts, which can strain national budgets and shift priorities away from other areas of economic development.
- Tourism Industry Decline (観光産業の衰退)
- Countries dependent on tourism can suffer significant economic losses when natural disasters damage key tourist destinations. Recovery from such events can take years, leading to lost revenue and job cuts in the sector.
- Increased Investment in Disaster Resilience (災害対策への投資増加)
- In the long term, natural disasters often prompt governments and industries to invest in disaster-resilient infrastructure, such as flood defenses and earthquake-resistant buildings. While costly, these investments can stimulate economic growth and reduce future risks.
- Global Market Volatility (世界市場の不安定化)
- Natural disasters can create uncertainty and volatility in global markets. Investors may react to disasters by pulling funds from affected regions or industries, leading to stock market fluctuations and currency depreciation in vulnerable economies.
論理展開・観点(日本語)
- 経済への直接的なダメージ:自然災害によってインフラ、建物、農作物が破壊され、修復費用や経済活動の停止によって経済にダメージを与える。
- 供給チェーンの混乱:災害は、世界的な供給チェーンを中断させ、生産や輸送に遅れが生じる。
- 保険業界への負担:自然災害による保険金の支払いが増え、保険業界や金融市場に影響を与える。
How Do Natural Disasters Affect the Global Economy?
Natural disasters have a significant impact on the global economy in several ways. First, they cause direct economic damage by destroying infrastructure, buildings, and agricultural land. Countries hit by natural disasters often have to spend vast amounts of money on rebuilding efforts, which can strain their budgets and slow down economic growth. Additionally, natural disasters can disrupt local businesses and industries, causing a temporary halt in economic activity, which affects not only the affected country but also its trading partners.
Another way natural disasters affect the global economy is by disrupting supply chains. Many industries rely on global supply chains, and when a disaster occurs, it can delay production and transportation. For example, a hurricane in one country can affect the delivery of raw materials to another country, causing delays in manufacturing and increased costs for businesses worldwide.
Lastly, the insurance industry is heavily affected by natural disasters. Insurance companies are often required to pay out large sums of money to cover the damages caused by these events. This can put financial pressure on the insurance industry and can also lead to increased premiums for businesses and individuals. In conclusion, natural disasters have widespread economic consequences, affecting not only the affected countries but also the global economy through supply chain disruptions and financial burdens on the insurance industry. (218 words)
自然災害は世界経済にどのような影響を与えますか?
自然災害は、さまざまな方法で世界経済に大きな影響を与えます。まず、インフラや建物、農地が破壊されることで、直接的な経済損失が発生します。自然災害に見舞われた国は、復興に莫大な資金を投入する必要があり、これが予算に負担をかけ、経済成長を鈍化させることがあります。さらに、地元の企業や産業が一時的に停止することで、被災国だけでなく、その貿易相手国にも影響を与えます。
次に、自然災害は供給チェーンに混乱をもたらします。多くの産業は世界的な供給チェーンに依存しており、災害が発生すると生産や輸送に遅れが生じます。たとえば、ある国で発生したハリケーンが、別の国への原材料の供給を遅らせ、製造の遅延やコストの増加を引き起こすことがあります。これは、世界中の企業に影響を与えます。
最後に、保険業界も自然災害によって大きな影響を受けます。保険会社は、自然災害による損害を補償するために、多額の保険金を支払う必要があります。これが保険業界に財政的な負担をかけるだけでなく、企業や個人の保険料が増加する可能性もあります。結論として、自然災害は、供給チェーンの混乱や保険業界への財政的負担を通じて、被災国だけでなく、世界経済全体に広範な影響を及ぼします。
質問 2: Should governments provide subsidies to struggling industries?
政府は困難な状況にある産業に補助金を提供すべきでしょうか?
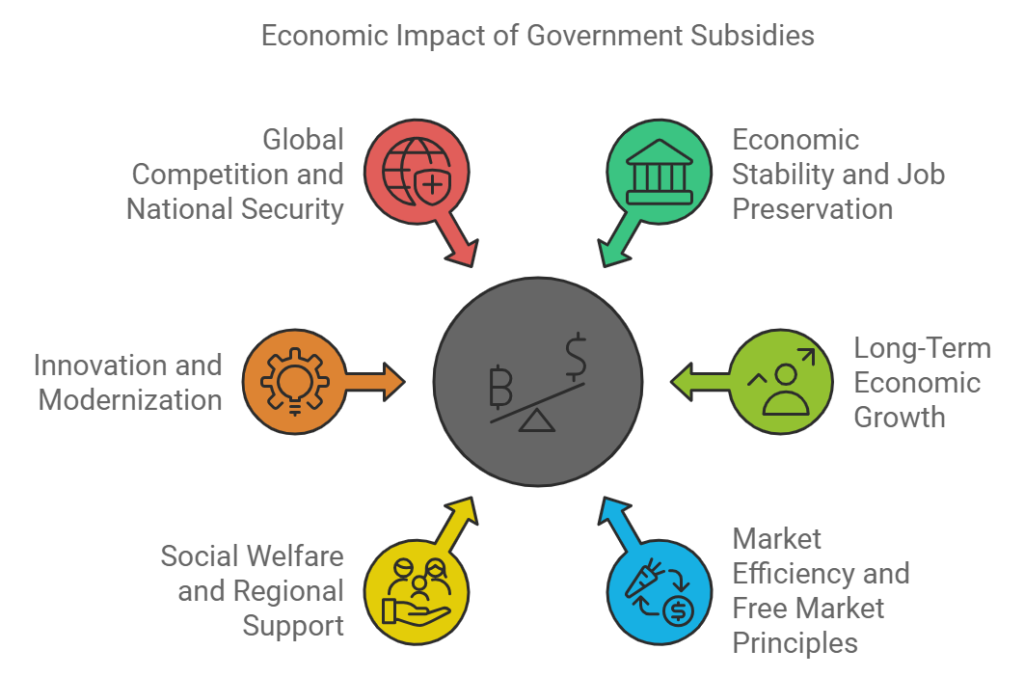
観点 (Perspectives)
- Economic Stability and Job Preservation (経済の安定と雇用の維持)
- Pro: Government subsidies can help struggling industries stay afloat during economic downturns, protecting jobs and preventing mass unemployment. This can stabilize local economies and prevent further economic decline.
- Con: Providing subsidies may encourage inefficient industries to continue operating when they should adapt or transition to more sustainable business models, ultimately distorting market competition.
- Long-Term Economic Growth (長期的な経済成長)
- Pro: Subsidies can be a short-term investment to ensure long-term economic growth. By helping key industries recover, governments can safeguard sectors essential for national infrastructure and future development.
- Con: Continuous financial support to struggling industries might lead to government dependency, preventing necessary innovation and progress. In some cases, this could slow down the shift toward emerging, high-growth industries.
- Market Efficiency and Free Market Principles (市場の効率性と自由市場原則)
- Pro: In times of crisis, such as global pandemics or financial recessions, government intervention through subsidies can correct market failures and provide critical support where private investment falls short.
- Con: Subsidies can interfere with free market principles, potentially leading to unfair competition. Industries that are not profitable without government support may continue to drain public funds without contributing effectively to economic growth.
- Social Welfare and Regional Support (社会福祉と地域支援)
- Pro: In regions heavily reliant on a single industry, government subsidies can prevent economic collapse, ensuring the well-being of communities and maintaining public services dependent on the economic activity of that sector.
- Con: Focusing subsidies on struggling industries might take away resources that could be better spent on public services, education, or healthcare, potentially causing a misallocation of national funds.
- Innovation and Modernization (イノベーションと現代化)
- Pro: Subsidies can be used strategically to support industries in transitioning toward more sustainable and innovative business practices, encouraging research and development, and fostering modernization.
- Con: If subsidies are not carefully allocated, they may end up supporting outdated technologies or industries that resist innovation, limiting overall economic progress and adaptation to global market trends.
- Global Competition and National Security (国際競争力と国家安全保障)
- Pro: Some industries are critical for national security and global competitiveness, such as energy, technology, and defense. Subsidies ensure these industries remain competitive on a global scale, protecting national interests.
- Con: Excessive reliance on subsidies can make industries less competitive internationally, as they may become less efficient compared to those in countries with fewer government interventions.
論理展開・観点(日本語)
- 経済の安定化:政府が補助金を提供することで、重要な産業が崩壊するのを防ぎ、経済の安定を保つ。
- 長期的な依存のリスク:補助金に依存することで、企業が効率的で持続可能な運営を目指さなくなる可能性がある。
- 資金の適切な配分:政府資金をどの産業にどのように配分するかが重要で、不公平な補助金は競争力を損なう可能性がある。
Should Governments Provide Subsidies to Struggling Industries?
I believe that governments should provide subsidies to struggling industries, but only under certain conditions. One reason is that some industries are vital to the national economy. For example, industries such as agriculture, transportation, and manufacturing provide essential goods and services that people rely on. If these industries collapse, it could lead to widespread unemployment and disrupt the economy. By providing subsidies, governments can help these industries survive difficult periods and protect jobs.
However, subsidies should not be given without careful consideration. One potential problem is that companies may become too dependent on government support. If an industry relies too much on subsidies, it may not make the necessary changes to become more efficient or competitive in the long term. Therefore, governments should ensure that subsidies are temporary and linked to clear goals, such as improving sustainability or innovation.
In conclusion, while subsidies can be useful in helping struggling industries recover, they should be used carefully. Governments must strike a balance between providing temporary financial support and encouraging industries to become more self-sufficient and competitive in the future. (178 words)
政府は困難な状況にある産業に補助金を提供すべきでしょうか?)
私は、政府が困難な状況にある産業に補助金を提供するべきだと考えていますが、それは特定の条件に基づいて行われるべきです。理由の一つは、いくつかの産業は国の経済にとって非常に重要であるという点です。例えば、農業、運輸、製造業などの産業は、人々が依存している必需品やサービスを提供しています。これらの産業が崩壊すると、大規模な失業が発生し、経済に混乱をもたらす可能性があります。政府が補助金を提供することで、これらの産業が困難な時期を乗り越え、雇用を守ることができます。
しかし、補助金は慎重に検討して与えられるべきです。問題の一つは、企業が政府の支援に依存しすぎる可能性があることです。もし産業が補助金に依存しすぎると、長期的には効率的で競争力のある運営を目指さなくなるかもしれません。そのため、政府は補助金を一時的なものとし、持続可能性や革新を促進する明確な目標に結びつけるべきです。
結論として、補助金は困難な産業を回復させるために役立つことがありますが、慎重に使用する必要があります。政府は、一時的な経済支援を提供する一方で、産業が将来的に自立し、競争力を高められるようにバランスを取らなければなりません。
質問 3: What is the impact of income inequality on society?
所得格差が社会に与える影響は何ですか?
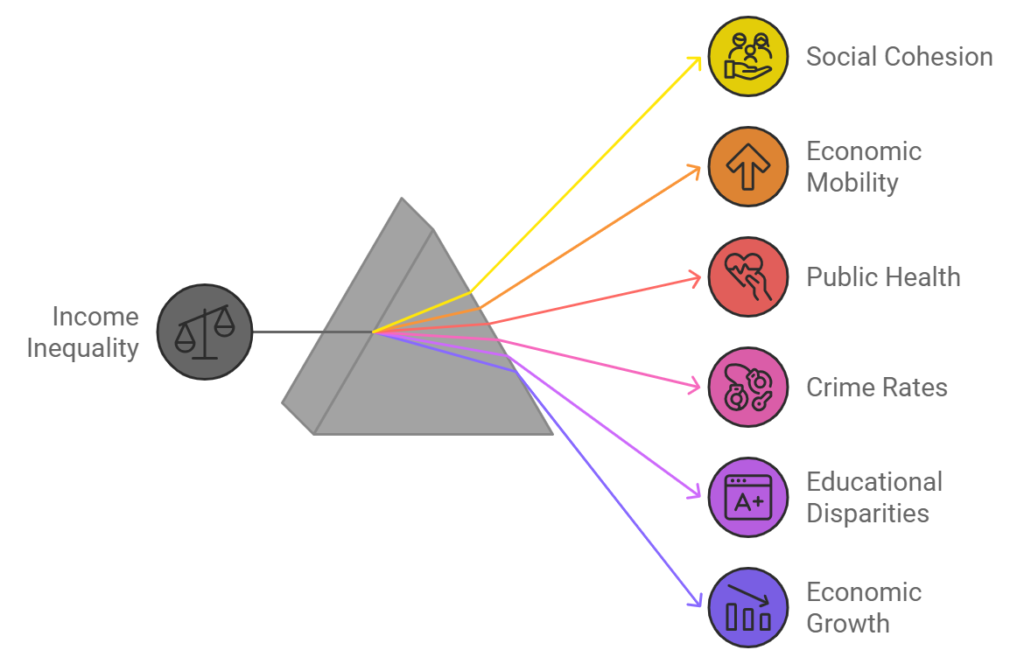
論理展開・観点(日本語)
- 社会的不安定の増加:所得格差が広がることで、貧困層が増加し、社会的な不満や犯罪率の上昇につながる可能性がある。
- 経済成長への悪影響:所得格差は消費を抑制し、全体的な経済成長を鈍化させることがある。
- 社会的流動性の低下:格差が固定化すると、貧困層が中流階級に移行する機会が減少し、社会の分断が深まる。
What Is the Impact of Income Inequality on Society
I believe that income inequality has a significant impact on society, particularly in terms of social stability and economic growth. One major effect of income inequality is the increase in social unrest. When the gap between the rich and poor widens, lower-income populations may feel left behind. This can lead to frustration and resentment, and even increase crime as people struggle to meet their basic needs. A society with high levels of inequality is more likely to experience social conflicts.
Another negative effect of income inequality is its impact on economic growth. In an unequal society, lower-income individuals have less disposable income, which reduces overall demand for goods and services. This can slow down economic growth, as businesses may struggle to sell their products. High levels of inequality can also limit access to education and opportunities for upward mobility, preventing people from improving their economic situations and contributing fully to the economy.
Finally, income inequality affects social mobility. In a society with large income gaps, it becomes more difficult for people from lower-income backgrounds to move up the social ladder. This lack of opportunity can lead to a rigid class structure, where wealth and privilege are concentrated in the hands of a few. In conclusion, income inequality has far-reaching consequences for both social stability and economic progress, making it a critical issue that needs to be addressed. (227 words)
所得格差が社会に与える影響は何ですか?
私は、所得格差が社会に大きな影響を与えると考えています。特に、社会の安定性と経済成長において顕著です。所得格差の主な影響の一つは、社会的な不安の増加です。富裕層と貧困層の格差が拡大すると、低所得層は取り残されたと感じることがあります。これにより、フラストレーションや不満が生まれ、犯罪が増加する可能性もあります。格差が大きい社会では、社会的な対立が生じやすくなります。
もう一つの負の影響は、経済成長に対する影響です。格差が大きい社会では、低所得層は可処分所得が少ないため、全体的な消費が抑制されます。これにより、企業が製品を販売しにくくなり、経済成長が鈍化する可能性があります。また、所得格差が広がると、教育や社会的な上昇の機会が制限され、人々が経済的に向上し、経済に完全に貢献することが難しくなります。
最後に、所得格差は社会的流動性にも影響を与えます。大きな所得格差がある社会では、低所得層が社会階層を上昇させるのが難しくなります。このような機会の欠如は、富や特権が少数の人々に集中し、社会が硬直化する原因となります。結論として、所得格差は社会の安定性や経済の進歩に広範な影響を与えるため、重要な課題として対処する必要があります。
単語・フレーズ・文法表現解説
- disposable income: 「可処分所得」
生活費を差し引いた後に残る、自由に使える収入を指す言葉です。所得格差がある社会では、低所得者層の可処分所得が少なく、消費に回せるお金が少ないため、経済活動が停滞する原因となります。 - upward mobility: 「社会的流動性、上昇の機会」
人々が低所得階層から中流・高所得層へと上昇するチャンスや、社会的な階層を上昇する機会を指します。所得格差が広がると、こうした上昇の機会が減少し、社会が固定化されるリスクが高まります。 - rigid class structure: 「硬直した階級構造」
社会における階級の固定化を表す言葉で、階級間の移動が難しくなり、貧富の差が固定化される状況を説明する際に使用されます。 - far-reaching consequences: 「広範な影響」
物事が社会全体に幅広く及ぼす影響を表現するフレーズです。所得格差が個人レベルだけでなく、社会全体や経済にも影響を与えることを強調する際に使います。
質問 4: How do online shopping platforms affect traditional brick-and-mortar stores?
オンラインショッピングプラットフォームは従来の店舗にどのような影響を与えていますか?
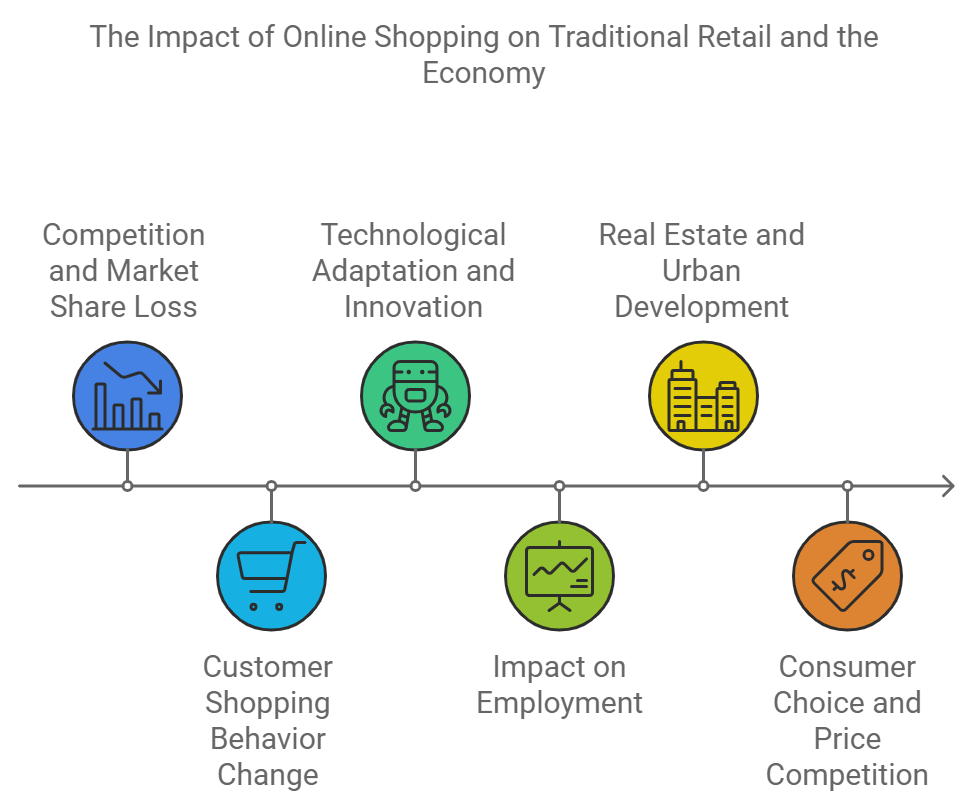
論理展開・観点(日本語)
- 売上の減少:オンラインショッピングの普及により、従来の店舗が顧客を失い、売上が減少している。
- 消費者の利便性:オンラインプラットフォームは、24時間いつでも利用でき、価格比較も容易であるため、消費者にとって便利な選択肢となっている。
- 変化への対応:従来の店舗もオンラインサービスやデジタル技術を取り入れて、新しい購買体験を提供することで競争力を保とうとしている。
How Do Online Shopping Platforms Affect Traditional Brick-and-Mortar Stores?
I believe that online shopping platforms have had a significant impact on traditional brick-and-mortar stores. One of the biggest effects is the reduction in sales for physical stores. As online shopping becomes more popular, many customers are choosing the convenience of shopping from home. This has led to a decrease in foot traffic for physical stores, which in turn has reduced their sales and profits. For small businesses, this shift can be particularly damaging, as they may not have the resources to compete with large online retailers.
Another impact is that online platforms provide consumers with greater convenience. Shoppers can browse products, compare prices, and make purchases 24/7 without leaving their homes. This ease of use makes online shopping an attractive option for many people. As a result, traditional stores are finding it harder to attract customers who now prioritize convenience and price over in-person shopping experiences.
However, brick-and-mortar stores are adapting to these changes by integrating digital services into their business models. Many stores now offer online ordering, home delivery, or in-store pickup options to remain competitive. In conclusion, while online shopping platforms have created challenges for traditional stores, those that embrace digital transformation can still find success in the changing retail landscape. (204 words)
オンラインショッピングプラットフォームは従来の店舗にどのような影響を与えていますか?
私は、オンラインショッピングプラットフォームが従来の店舗に大きな影響を与えていると考えています。その最大の影響の一つは、実店舗の売上減少です。オンラインショッピングがますます普及する中、多くの顧客が自宅から買い物をする便利さを選んでいます。この結果、実店舗の来客数が減少し、それに伴い売上や利益も減少しています。特に中小企業にとっては、この変化が大きな打撃となり、大手のオンライン小売業者と競争するのが難しくなります。
もう一つの影響は、オンラインプラットフォームが消費者により大きな利便性を提供していることです。消費者は、24時間いつでも商品を閲覧し、価格を比較し、購入することができるため、オンラインショッピングは非常に魅力的な選択肢となっています。この利便性により、従来の店舗は顧客を引き寄せるのが難しくなり、消費者は便利さや価格を優先するようになっています。
しかし、実店舗もこれらの変化に対応しつつあります。多くの店舗がオンライン注文や配送サービス、店頭での受け取りオプションを提供し、競争力を維持しようとしています。結論として、オンラインショッピングプラットフォームは従来の店舗に課題をもたらしていますが、デジタル変革を取り入れることで、店舗も依然として成功を収めることができると考えられます。
質問 5: Is globalization beneficial or harmful to local economies?
グローバリゼーションは地域経済にとって有益ですか、それとも有害ですか?
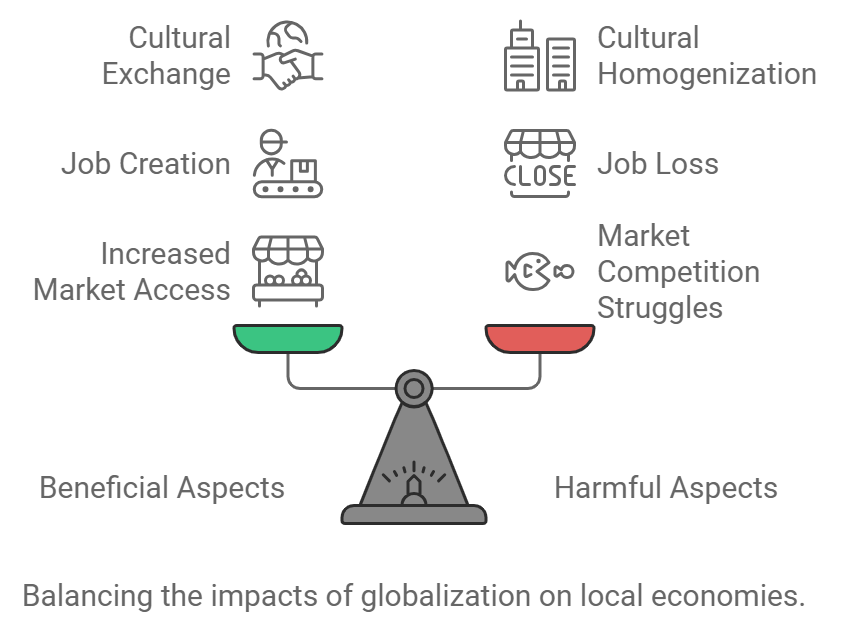
論理展開・観点(日本語)
- 有益な側面:グローバリゼーションにより、地域経済は国際市場にアクセスし、貿易や投資が増加し、経済成長が促進される。
- 有害な側面:一方で、グローバリゼーションにより地域の小規模企業が大規模な国際企業に圧倒され、地域特有の産業が衰退するリスクがある。
- バランスの重要性:地域経済は、グローバリゼーションの恩恵を受けるために競争力を高めつつ、地域固有の価値を守ることが重要である。
Is Globalization Beneficial or Harmful to Local Economies?
I believe that globalization has both beneficial and harmful effects on local economies. One of the main benefits of globalization is that it allows local economies to access international markets. Through globalization, local businesses can expand their customer base and increase exports, leading to greater economic growth. Additionally, foreign investments can bring new technologies, knowledge, and skills to the local economy, which can help modernize industries and create new job opportunities.
However, globalization also presents some challenges. One of the biggest drawbacks is that local businesses may struggle to compete with large multinational corporations. These corporations often have more resources and can offer lower prices, making it difficult for small businesses to survive. As a result, some local industries may decline or disappear entirely. Furthermore, globalization can lead to the loss of cultural identity as local products and traditions are replaced by global brands.
In conclusion, while globalization offers significant opportunities for local economies to grow and innovate, it also poses challenges that must be managed carefully. Governments and businesses need to strike a balance between embracing globalization and protecting local industries and cultural heritage to ensure that the benefits outweigh the risks. (193 words)
グローバリゼーションは地域経済にとって有益ですか、それとも有害ですか?
私は、グローバリゼーションが地域経済に対して有益な側面と有害な側面の両方を持っていると考えています。グローバリゼーションの主な利点の一つは、地域経済が国際市場にアクセスできることです。グローバリゼーションを通じて、地域企業は顧客基盤を拡大し、輸出を増加させ、経済成長を促進することができます。さらに、外国からの投資は新しい技術や知識、スキルを地域にもたらし、産業を近代化し、新たな雇用機会を創出する助けとなります。
しかし、グローバリゼーションにはいくつかの課題もあります。最大の欠点の一つは、地域の企業が大規模な多国籍企業と競争するのが難しいという点です。これらの企業はより多くの資源を持ち、価格を低く抑えることができるため、小規模な企業が生き残るのは困難です。その結果、一部の地域産業は衰退したり、完全に消滅したりする可能性があります。さらに、グローバリゼーションは地元の文化的アイデンティティの喪失につながることもあり、地域の製品や伝統が世界的なブランドに取って代わられることがあります。
結論として、グローバリゼーションは地域経済が成長し革新するための重要な機会を提供しますが、慎重に管理しなければならない課題も存在します。政府や企業は、グローバリゼーションを受け入れる一方で、地域産業や文化的遺産を保護するバランスを取る必要があり、利益がリスクを上回るようにすることが重要です。




